Earned Value Methods (EVM) - Explained
Earned value methods, also called performance measurement algorithms, techniques, or work completion Algorithms, are based on industry-standard EV methods. They can be optionally assigned to each activity using the Barchart Editor. The EVM field is available as a column and as a field on the EVM tab of the Activity Information pane. To measure your progress at the activity level, you report the actual % or you can apply the Safran EV Methods to set actual progress calculations and measure the completed work. The earned value calculations are performed when you run the Status update, and the result is stored in the Actual % Complete field.
Earned Value Methods are only available to activites in single/standalone projects.
You may apply or edit the EVM in the Barchart Editor either by adding a column named Earned Value Method or by using the EVM Tab in the Activity Information View.
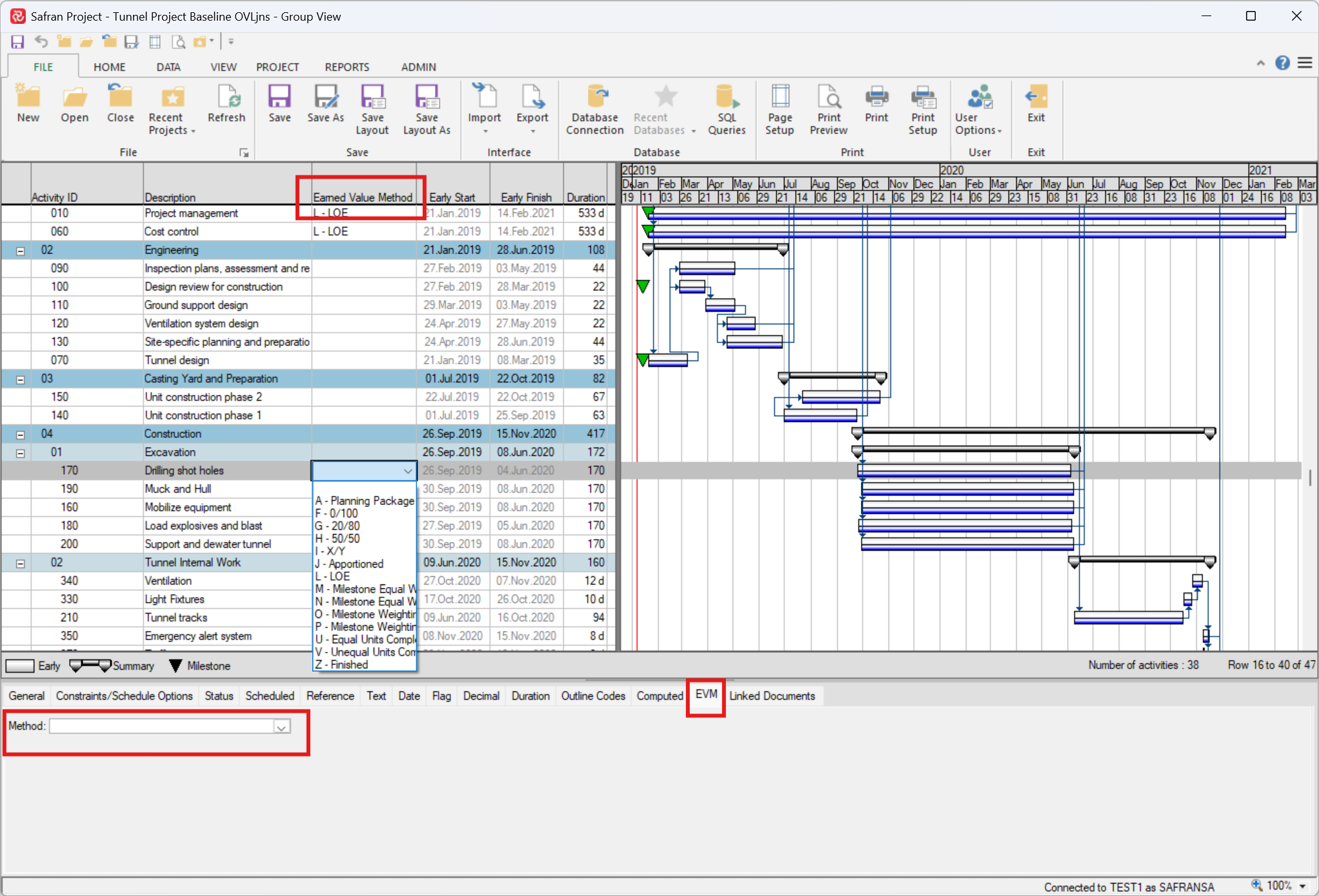
EVM Overview
The Earned Value (EV) method you assign to an activity depends on the defined task type. EV methods objectively assess the work completed, reducing the subjective nature of status reporting and progress evaluation. In addition to the Earned Value Methods, Safran Project includes an "Always on Schedule" method. To set an activity as always on schedule, check the "Always on Schedule" box in the Activity Information pane of the Barchart Editor. Activities marked as always on schedule are automatically assigned their planned value as Earned Value. This method benefits project activities that do not produce tangible outcomes that can be measured objectively, such as Project Management tasks. An on-schedule activity will have no Schedule Variance, and this condition corresponds to a Level of Effort (LOE) technique or method.
| EV Method | Description |
|---|---|
| A | Planning Package |
| F | 0/100 |
| G | 20/80 |
| H | 50/50 |
| I | X/Y (requires parameter) |
| J | Appointed (requires parameter) |
| M | Milestone Equal (requires parameter) |
| N | Milestone Equal Weight % Complete (requires parameter) |
| O | Milestone Weighting (requires parameter) |
| P | Milestone Weighting % Complete (requires parameter) |
| U | Equal Units Complete (requires parameter) |
| V | Unequal Units Complete (requires parameter) |
| Z | Finished |
EVM Detailed
This section describes the various EV Methods and calculations. It includes a general description, the earned value calculation, a logic test, and the type of activity the earned value method is suited for.
A - Planning Package
Nothing can be earned; the result will always be 0.
This is ideal for planning tasks or activities intended for future implementation but not yet detailed enough to be broken down into work plans and specific tasks. A budget may be assigned to this planning package or task. Additionally, it can be used if the user wants to prevent any value from being earned for the activity at this stage.
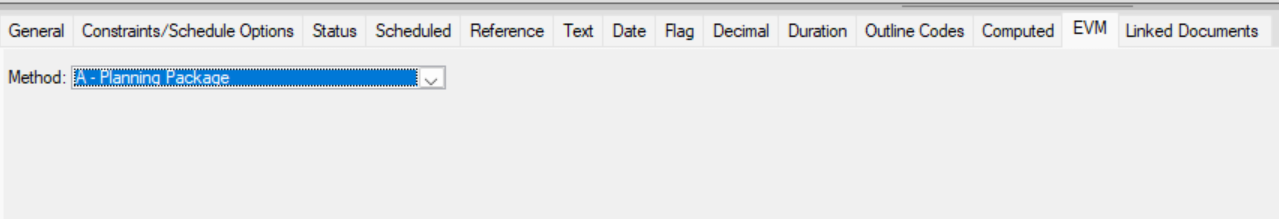
F - 0/100
This is a measurable effort. A complete 100% will be automatically earned upon completion of the activity.
You will earn 100% when the Actual % Complete is reported as 100% or a Current Actual Finish date is provided. No credit will be earned if the reported percentage is between 0 and 99%.
This criterion should only apply to activities spanning a single cutoff period or a milestone. The task is considered complete only when it is either fully finished or not started.
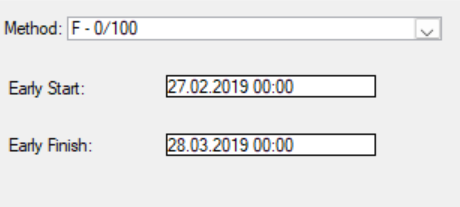
G - 20/80
This is a measurable effort. You will automatically earn 20% when an activity starts, and 100% will be automatically earned when the activity is finished.
You earn 20% when the Actual % Complete exceeds 0 or when a Current Actual Start date exists. The remaining 80%, which brings the total to 100%, is earned when the Actual % Complete reaches 100%.
This approach is ideal for activities that span two cutoff periods, especially when the work is backloaded, meaning more value is awarded at the end of the activity.
H - 50/50
This is a measurable effort. Fifty percent (50%) will be automatically earned when an activity starts, and one hundred percent (100%) will be automatically earned when the activity is finished.
Fifty percent is earned when the Actual % Complete exceeds 0%. One hundred percent is earned when the Actual % Complete equals 100%. This represents the remaining fifty percent.
This approach is ideal for activities that span two cutoff periods, with work distributed evenly across both periods. Value is earned equally for the two periods, provided the second cutoff completes the activity.
I - X/Y (Requires Parameter)
The X in the X/Y format indicates the value earned when an activity starts. The Y represents the remaining value earned when the activity finishes. This number should consist of digits only—for example, 30/70. This method is more flexible, allowing the planner to choose how progress is calculated instead of methods 0/100, 20/80, and 50/50, where it is predefined.
This approach is measurable. A percentage (X%) will be automatically earned when the activity begins, and 100% will be earned upon completion. X% is earned when the Actual % Complete is greater than 0%, while 100% is earned when the Actual % Complete reaches 100%. This reflects the remaining Y%.
This method is ideal for activities that span two reporting periods. It allows the user to specify how much value is earned when the activity commences in the first reporting period and how much is earned in the second period upon the activity's completion.
J - Apportioned (Requires Parameter)
Select referenced activity tasks.
The calculated percentage is based on the sum of earned value from the referenced activities divided by the total budget at completion.
This approach is ideal for activities that earn value based on the performance of other referenced activities. For example, consider a Quality Assurance activity that earns value based on the product being developed. The Quality Assurance team can conduct more tests as more of the product is built.
M - Milestone Equal Weight (Requires Parameter)
Select the applicable milestones or activities.
The percentage is determined by dividing the number of completed milestones or activities by the total number of referenced milestones or activities.
This method is ideal for activities linked to milestones or activities with short durations, where each referenced milestone or activity carries equal weight. Typically, the source activity is longer than two cutoffs. For example, in a software development project, value is earned as milestones representing various phases, such as requirements, analysis, design, and so on, are completed.
N - Milestone Equal Weight% Complete (Requires Parameter)
Select the applicable milestones or activities.
The calculated percentage is determined by taking the sum of the Actual % Complete for each referenced milestone or activity and dividing it by the total number of referenced milestones or activities.
This method is ideal for activities linked to milestones or activities with longer durations, as too much time may pass for the referenced milestone or activity to earn credit. Each referenced milestone or activity carries equal weight. Typically, the source activity spans more than two cutoff periods. An example would be a software development activity that accrues value as milestones representing various phases, such as requirements, analysis, design, etc., are achieved.
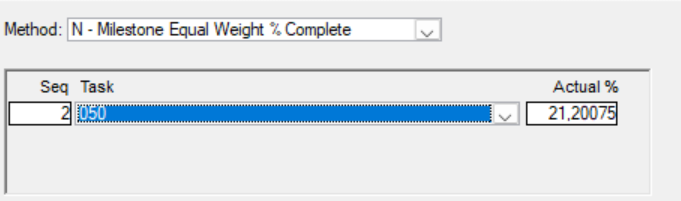
O - Milestone Weighting (Requires Parameter)
Select an activity or milestone and assign a weight to each one.
The percentage is determined by the number of completed milestones or activities multiplied by their respective weight, divided by the total weight of all referenced milestones or activities. This approach works well for activities linked to short-duration milestones or activities, where each may have varying weights.
Typically, the source activity lasts longer than two cutoffs. For example, in a software development project, value is accrued as milestones representing different phases, such as requirements, analysis, design, and so on, are completed. The effort required for these milestones may vary, meaning finishing the requirements phase could carry more weight than completing the analysis phase.
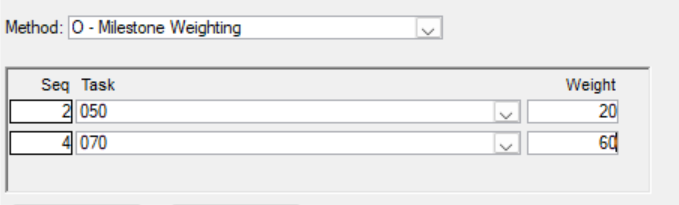
P - Milestone Weighting Percent Complete (Requires Parameter)
Select Activity or Milestone and add a weight factor.
The calculated percentage is based on the sum of the Actual % Complete, multiplied by their respective weights, and divided by the total number of referenced milestones or activities, also multiplied by their weights.
This method is particularly suitable for activities linked to milestones with longer durations, where significant time may pass without the referenced milestones earning credit. Additionally, each referenced milestone or activity may carry different weights. Typically, the source activity spans more than two cutoffs. For example, a software development project's value is earned as milestones representing various phases, such as requirements, analysis, design, etc., are completed. The effort devoted to these milestones may vary significantly, meaning completing the requirements phase could be valued more than completing the analysis phase.
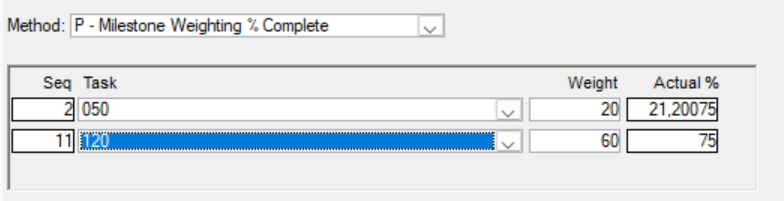
U -Equal Units Complete (Requires Parameter)
Please specify the total number of units and the number of units completed.
The percentage is determined by dividing the number of units completed by the total units planned.
This method is ideal for activities that produce a uniform number of units, where each unit is equally weighted. For example, if an activity involves the delivery of 10 documents and 4 documents are completed, then the earned value for the work would be 40%. Using this approach allows for better traceability than relying on a physical completion percentage.
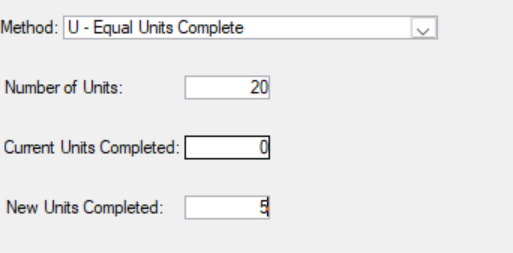
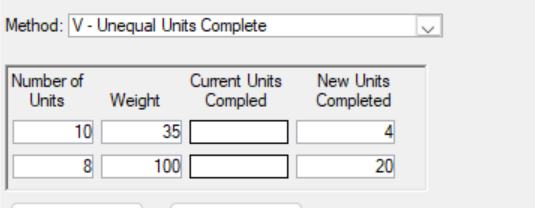
V - Unequal Units Complete (Requires Parameter)
Please enter the number of units, their respective weights, and the number of completed units.
The calculated percentage is determined by summing the product of the completed units and their weights, then dividing that total by the product of the planned units and their weights.
This method is beneficial for activities that yield several units, especially when some units have different levels of effort associated with them. For example, if an activity involves delivering 10 documents, where 5 require more effort, the computation would work as follows: If all 5 easier documents are finished. Still, the 5 more challenging ones remain; the earned value would be 33.3%. This approach provides better traceability than a simple physical percentage complete method and acknowledges that some units may carry more weight in terms of effort to complete.
Z- Finished
All results are earned, and the final result will always be 100.
This approach is ideal for activities that have been completed, allowing the user to close them out. It may also assist in setting up filters or other analytics.