Filters
Spotlight on the use of Filters in Safran
Download PDF: The use of Filters in Safran
Selecting Data (Filter)
While working in the Barchart Editor, Safran Project provides two features for narrowing down the amount of activities presented.
- Applying a 'Normal Filter'
- Using 'Auto-Filter' on displayed columns
Specifying Activity Selection Criteria
To select a data group, you must specify criteria familiar to all the entries in the group. Your selection criteria can be saved as named filters for later reuse. By choosing Filters from the HOME toolbar, you are given a window for selecting the activities to appear on the Barchart Editor. If no selection criteria are entered, all activities in the project are included.
Create a new filter
Selection criteria and filter expressions may get complicated and cumbersome to enter, so you may find it helpful to name and store your expressions for future use.
To create a new filter, click on the 'Filters ' icon.
![]()
Click 'New...'
Type in a filter name
Click 'Insert Row' and add your filter criteria.
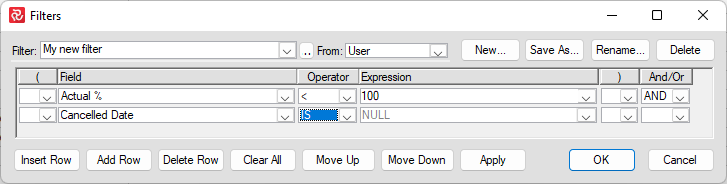
The 'APPLY' and the 'OK' buttons will save any modifications to your filter; the only difference is that 'OK' will close the filter window, while 'APPLY' leaves the window open. If you wish to modify a complex filter, it is recommended to first use the 'Save As...' option so you can go back to the old filter in case you are not happy with the new filter.
Remember that a filter could be used in layouts and reports, so changing an existing filter might have consequences you don't see in the current view.
Select a Filter
To select an existing filter, choose from the Filter drop-down list.
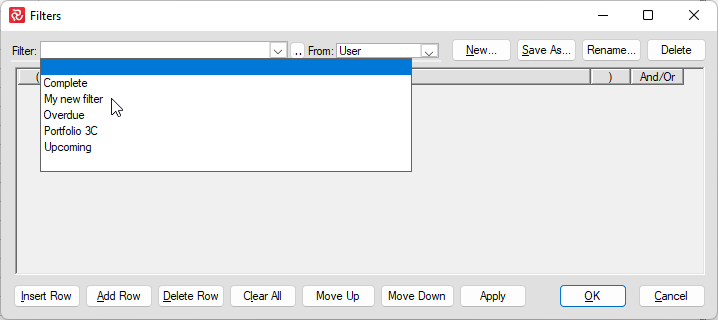
The 'Save As...' option allows you to modify and save an existing filter under a new name.
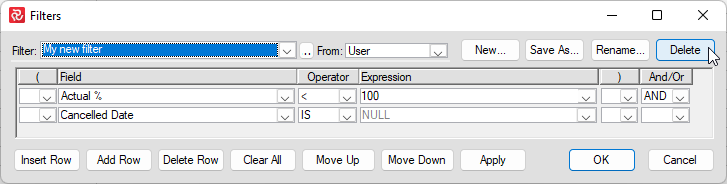
To remove a filter expression from the list of filters, select the filter from the drop-down box and press the Delete button.
Keep in mind that filters are 'universal' throughout Safran and may be used in all areas/functions of the system.
When used in a multi-user environment, a filter specified by one user will be available for all users on the system. Other users could choose and even modify/adjust the filter ad hoc. However, they would not be allowed to save changes to the original filter. The users would still be allowed to store the filter as their own.
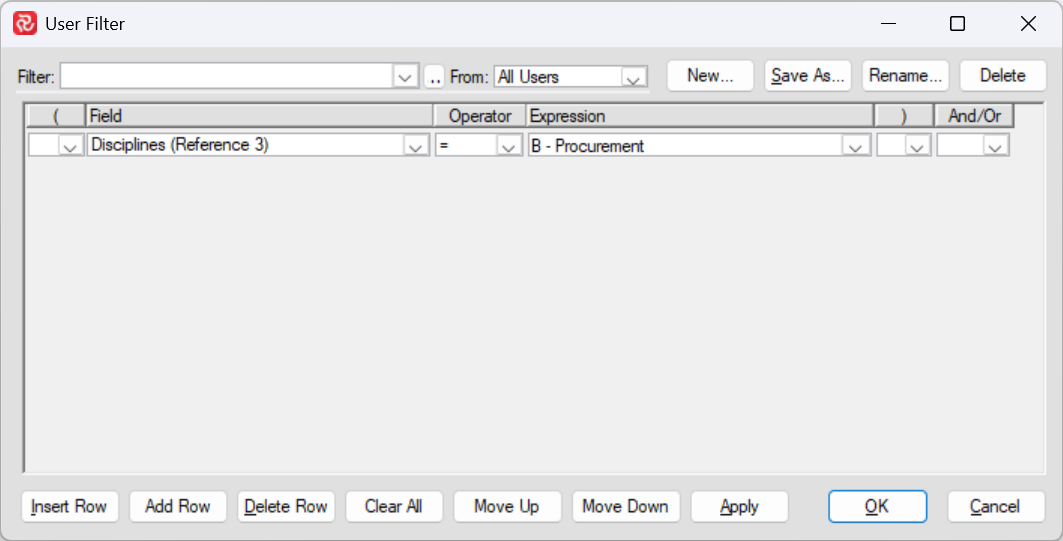
User filter
The 'User Filter' feature is available in Safran. This filter functions like a universal or default filter and is applied even if you haven't specifically selected a filter for a particular tool, such as the Barchart Editor, Report, or Assign Fields. This filtering option can be particularly useful when working on a large project, as it allows you to focus on a specific portion of the project while still filtering for specific activities.
In other words, you can use the 'User Filter' to isolate a subset of activities within a project. After applying the 'User Filter', you can further refine your results using a regular filter, an auto filter, or a combination of both to drill down into the details of the selected activities.
You can find the User Filter function on the Home tab of the ribbon, positioned to the right in the Editing area.
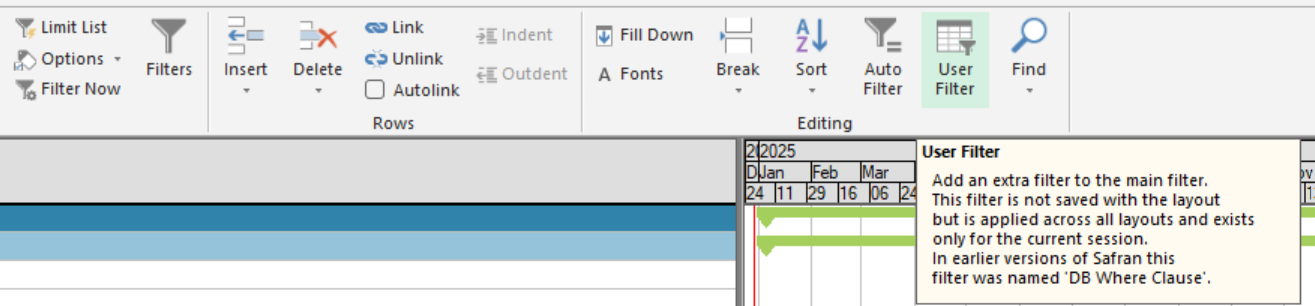
When you press the User Filter icon, the User Filter window opens, allowing you to select a filter.
When a User filter is activated, the User Filter icon on the ribbon is highlighted.
Remember that the User filter will be active for your current Safran session until you modify or turn it off/remove the filter conditions. It will be removed when you leave your Safran session.
The User Filter was named DB-where clause in Safran Project versions that predated version 7.
Auto filter
In addition to the filtering capabilities discussed above, Safran also has an 'Auto Filter' tool for the fields nominated in your Barchart layout. To switch the function on/off, select the tool from the Home/Editing portion of the ribbon.
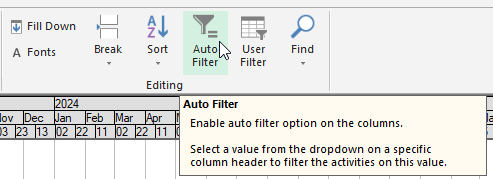
Or by right-clicking in the Column Header area and toggling 'Auto Filter' as shown below:
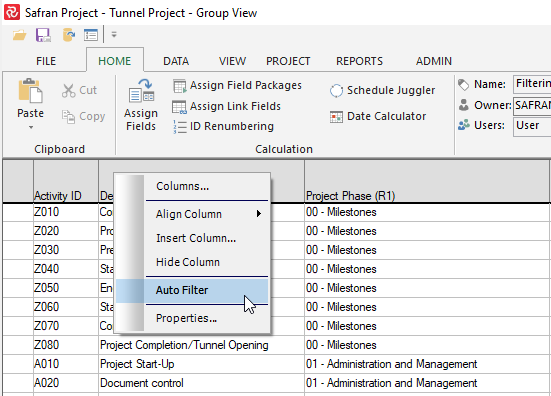
When an auto filter is turned on, a down arrow appears to the right in each column heading, indicating that auto filter capabilities are available.
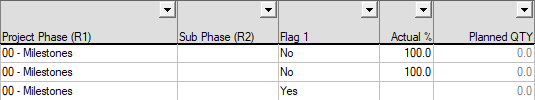
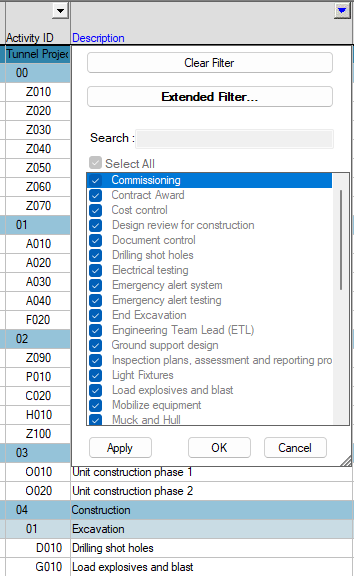
You can select relevant values from the column values drop-down in its simplest form. You can also apply an auto filter to multiple columns as required.
When an auto filter for a column is applied, the down arrow and header turn blue.
NULL means that there are no values in the cell. If you used the standard filter, the filter above would equal the operator 'IS NOT NULL.'
For flag fields, only two options (Yes/No) are available:
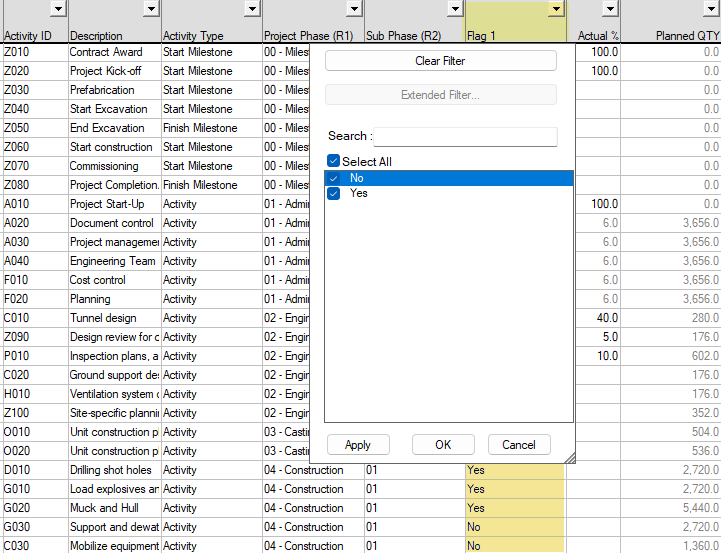
In a standard filter, the 'Search' field works as the operator 'Contains.'
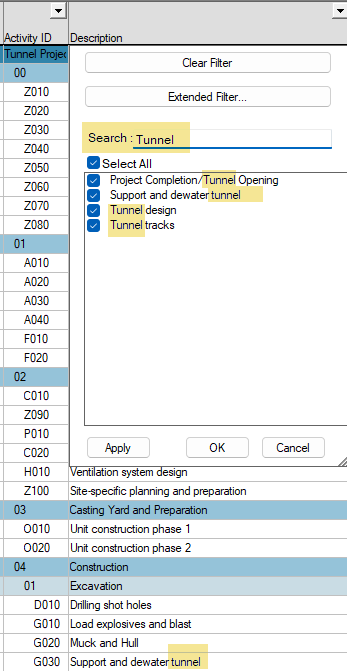
In addition to simple filtering, Safran provides you with more extensive capabilities similar to the standard functions discussed earlier.
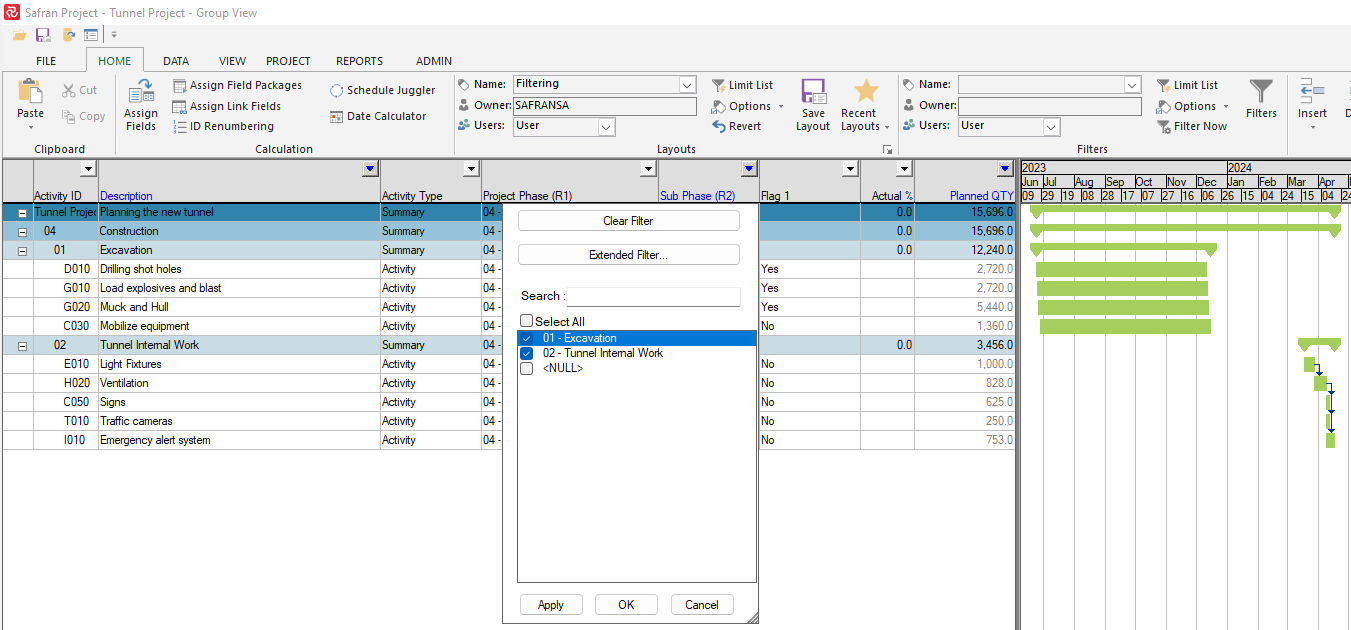
A standard filter panel is opened by selecting 'Extended Filter' in the Auto Filter panel, allowing you to specify a more extensive filter expression with relevant operators for the chosen field.
Once an 'Extended Filter' is specified, the existing simple selection is presented in light gray while the 'Extended Filter...' button is highlighted. To return to simple Auto Filter, press the 'Clear Filter' button.
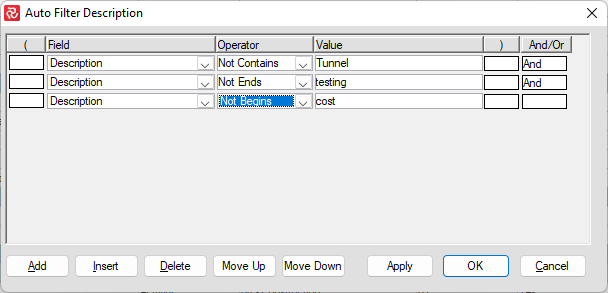
Filter Operators
| Operator | Meaning | Usage guideline |
|---|---|---|
| = | Equals | Valid for a column that contains text, numbers, or dates. Specify a single value or pick a value from the drop-down list. Results include only records where the data in the column matches the value in the filter. |
| <> | Not equal | Valid for a column that contains text, numbers, or dates. Specify a single value or pick a value from the drop-down list. Results include only records where the data in the column does not match the value in the filter. |
| < | Less than | Valid for a column that contains numbers or dates. Specify a single value. Results include only records where the data in the column is less than the value in the filter. |
| > | Greater than | Valid for a column that contains numbers or dates. Specify a single value. Results include only records where the data in the column is greater than the value in the filter. |
| <= | Less than or equal to | Valid for a column that contains numbers or dates. Specify a single value or multiple values. Results include only records where the data in the column is less than or the same as the value in the filter. |
| >= | Greater than or equal to | Valid for a column that contains numbers or dates. Specify a single value or multiple values. Results include only records where the data in the column is greater than or the same as the value in the filter. |
| IS NULL | no value | Valid for a column that contains text, numbers, or dates. Do not specify a value. The operator tests only for the absence of data in the column. Results include only records where there is no data in the column. |
| IS NOT NULL | contains a value | Valid for a column that contains text, numbers, or dates. Do not specify a value. The operator tests only for the presence of data in the column. Results include only records where there is data in the column. |
| Begins | value begins with | Valid for a column that contains text, numbers, or dates. Specify a single value. Results include only records where the data in the column begins with the value in the filter. |
| Not Begins | value does not begin with | Valid for a column that contains text, numbers, or dates. Specify a single value. Results include only records where the data in the column does not begin with the value in the filter. |
| Contains | value contains | Valid for a column that contains text, numbers, or dates. Specify a single value or multiple values. Results include only records where the data in the column contains the values in the filter. |
| Not Contains | value does not contain | Valid for a column that contains text, numbers, or dates. Specify a single value or multiple values. Results include only records where the data in the column does not contain the values in the filter. |
| Ends | value ends with | Valid for a column that contains text, numbers, or dates. Specify a single value. Results include only records where the data in the column ends with the value in the filter. |
| Not Ends | value does not end with | Valid for a column that contains text, numbers, or dates. Specify a single value. Results include only records where the data in the column does not end with the value in the filter. |
| IN | value equals X (or equals y) (or equals n) | Valid for a column containing text, numbers, or dates. Specify a single or multiple values (separating values with a comma). Results include only records where the data in the column matches the value(s) in the filter. |
| Not IN | value does not equal X (nor equals y) (nor equals n) | Valid for a column containing text, numbers, or dates. Specify a single or multiple values (separating values with a comma). Results include only records where the data in the column does not match the value(s) in the filter. |
These two filters will, for example, give you the same result:
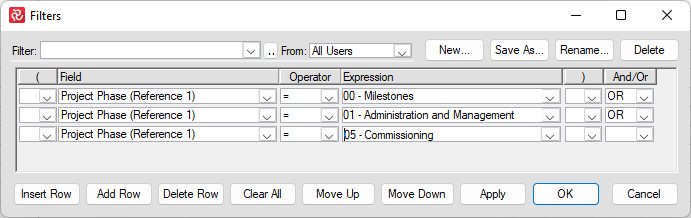
Depending on how complex your filter is, you might have to add parenthesis to ensure you get the selection that you want.
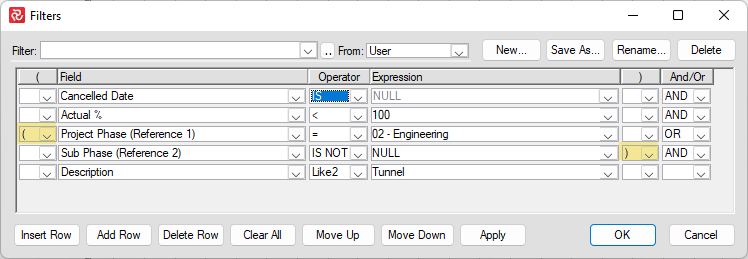
Using the 'Move up' / 'Move down' allows you to rearrange your filter. In the example below, the description row was moved up two rows. This filter will not work unless you modify it.
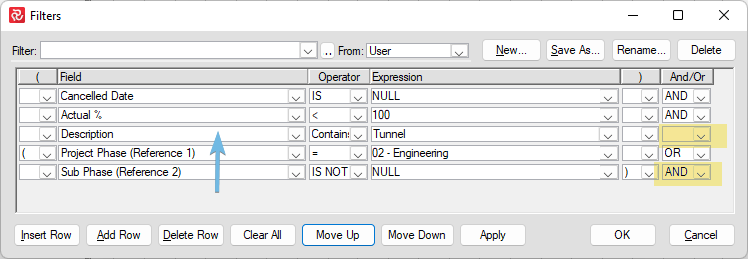
Even if you can save the filter without error, you should still check in the Barchart Editor that you have the desired selection before relying upon it in reports.
Logic based Filtering
The majority of the filtering capabilities in Safran are based on either activity information or user defined field values.
In addition to the above, Safran also provides logic based filtering capabilities; in other words, the ability to filter on information/field values related to your network logic and the CPM calculations.
The following logic related fields are available for use in filters:
| Field | Valid Values |
|---|---|
| Float Path | 1-n |
| Float Path Order | 1-n |
| Longest Path | Yes/No |
| Number of Predecessors | 0-n |
| Number of Successors | 0-n |
| Number of Disabled Predecessors | 0-n |
| Number of Disabled Successors | 0-n |
| Out of Sequence | Yes/No |
| Current Out of Sequence | Yes/No |
| All Predecessors Completed | Yes/No |
| Predecessors | Activity ID |
| Successors | Activity ID |
| Preceding Path | Activity ID |
| Succeeding Path | Activity ID |
Float Path fields
Safran's Multiple Float Path function can identify and flag multiple float paths where each activity is given a Float Path number/identifier and a Float Path Order number.
The Multiple Float Path calculation must be switched on for calculations to take place. This may be found on the Project ribbon by selecting Options from the Schedule tab.
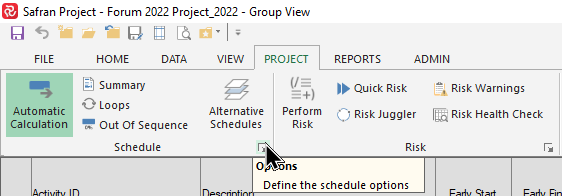
This opens the Schedule Options window where the Multiple Float Paths function may be switched on and configured as shown below:
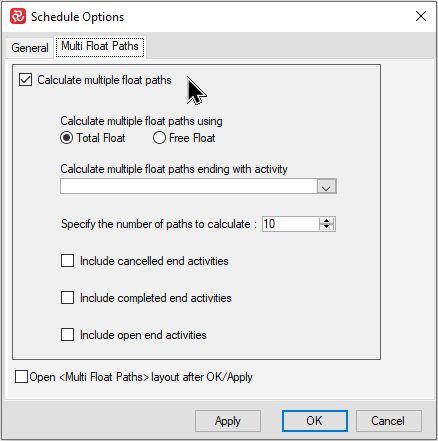
For more information on this topic please see: Multiple Float Paths
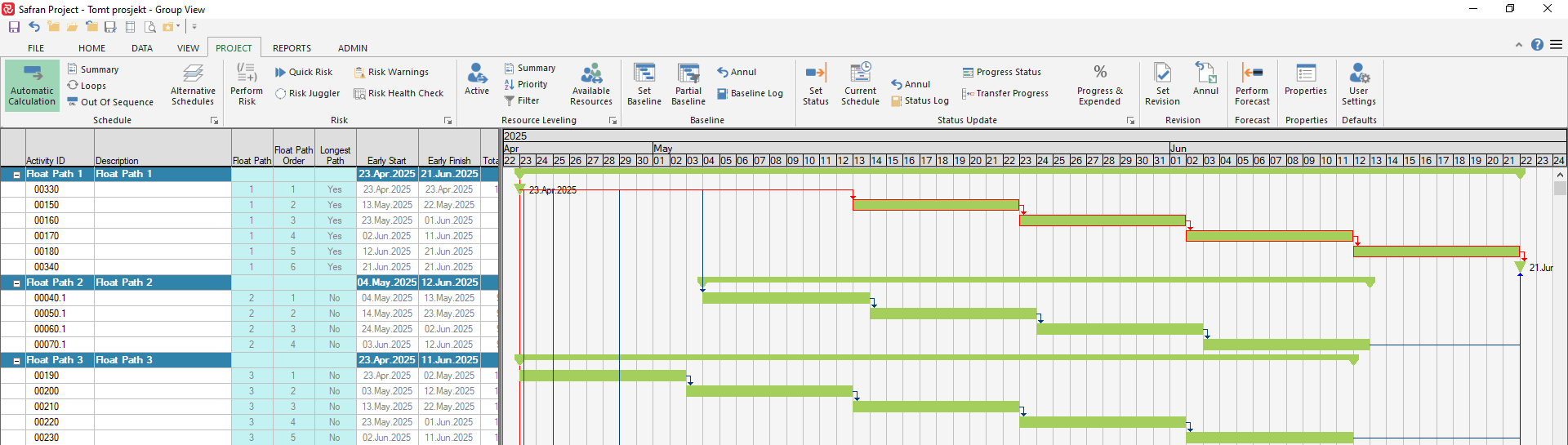
Float paths are numbered from 1 for the latest finishing path, 2 for the next latest and so on. Float Path Order is the logical order of each activity beginning with the logical first/earliest activity.
Selecting on Float Path i.e., Float Path=3, allows you to focus on the activities on a specific Float Path.
Longest Path is always calculated. If you select Longest Path=Yes, all activities along the longest path will be shown.
The picture below illustrates the calculation of the various float path fields:
Progress-related Logic fields
The ‘Out of Sequence’ field calculations take into consideration both progress and logic. An activity is considered out of sequence if the activity progress is >0% complete and one of the activitiy's immediate predecessors is incomplete (less than 100%).
The calculation for the Out of Sequence field is based on % Complete (PC), while the Current Out of Sequence field is based on Actual%.
The All Predecessors Completed field is set to Yes if all ‘immediate’ predecessors for an activity are 100% complete. If one or more of an activity’s ‘immediate’ predecessors is less than 100% complete, the field is set to No. This calculation is based on Actual%.
The picture below illustrates the ‘Out of Sequence’ and ‘All Predecessors Complete’ concepts:

Note that the All Predecessors Completed field for activity 00340 is set to No due to the fact that one of it’s predecessors, activity 00180.1 is incomplete.
Using these fields in a filter can help track down potential incorrect progress updating or in some cases even incorrect logic.
It also allows for the efficient validation of finish milestones, ie. the prerequisite for a 100% complete milestone that preceding activities must be completed.
The Number of Predecessors/Successors and Number of Disabled
Safran keeps track of how many immediate predecessors/successors each activity has. By filtering on these fields, ie Number of Predecessors > 20, you can easily identify areas in your schedule with a high density of links which in turn may suggest bottlenecks/areas of concern.
Safran also allows you to ‘temporarily’ modify the logic in your network in order to assess alternative scenarios by disenabling links between activities. By using the Number Disabled Predecessors/Successors field in a filter it’s easy to keep track of the use of disabled links.
The picture below illustrates the Number of Predecessors/Successors concepts:
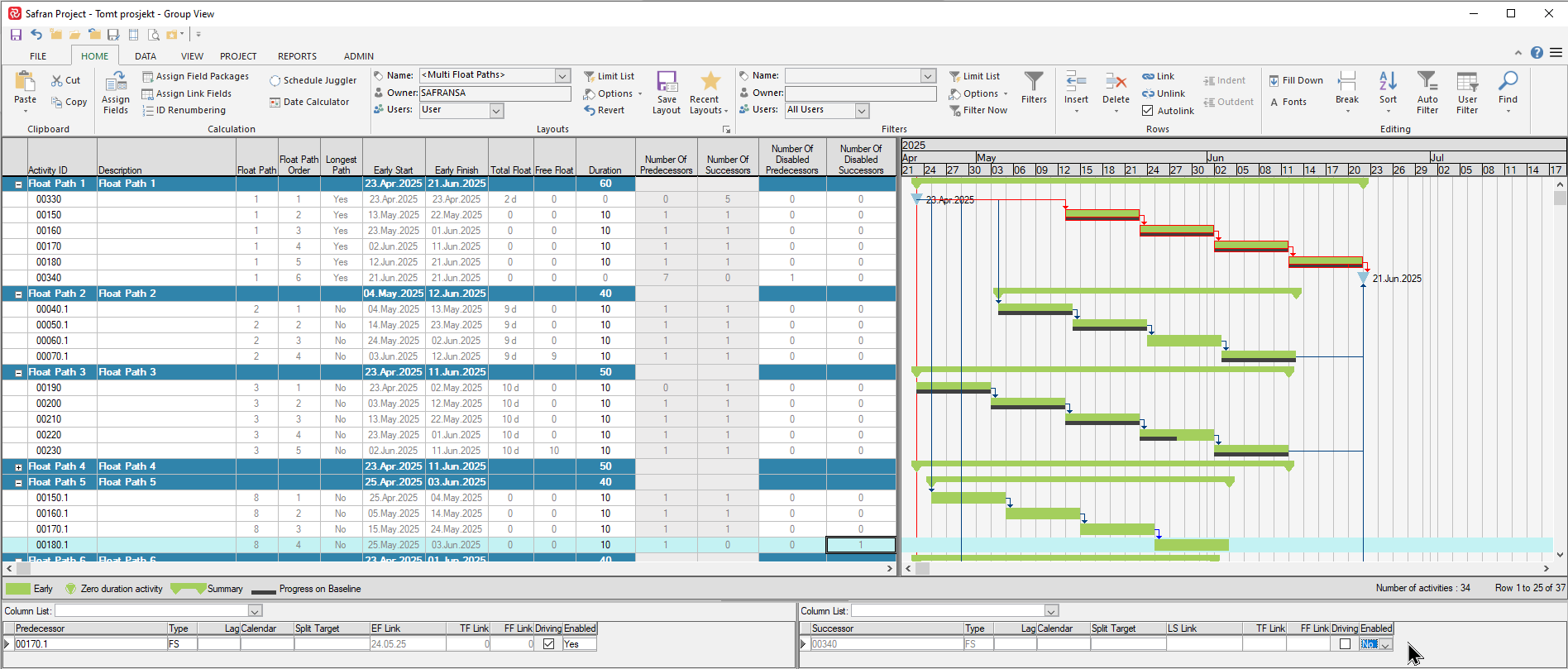
Note that activity 00340 has 1 disabled predecessor and activity 00180.1 has one disabled successor as the link between these activities has been disabled.
Predecessors/Successors and Preceding/Succeeding path
The Predecessors/Successors fields contain a list of an activity’s immediate predecessor/successor. If your project’s Activity ID contains coded information (i.e Discipline, System, etc.), you can use these fields in a filter to select specific types of activities and focus on the logic and validate the sequencing of activities.
In the example below the filter selects activities having a predecessor beginning with Z:
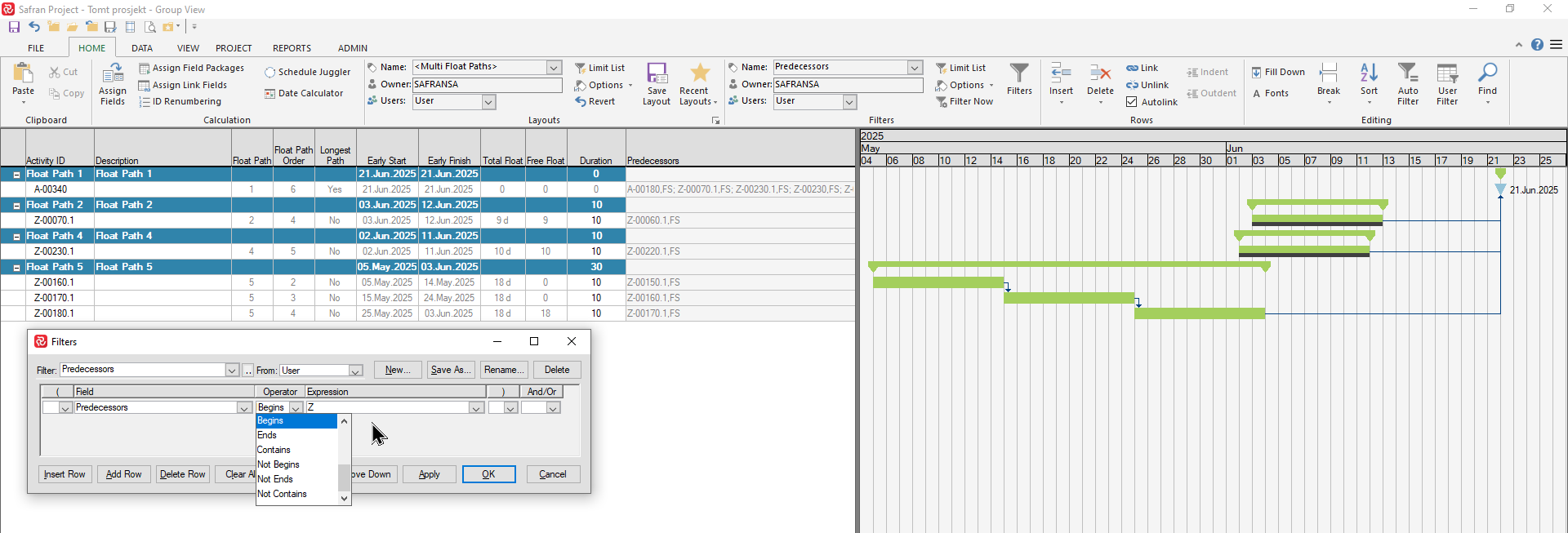
Whereas using the predecessors/successors fields in a filter by nature selects the first activity the Preceding/Succeeding Path of ‘field’ is much more powerful as it allows you to focus on all activities leading to/from a focus activity.
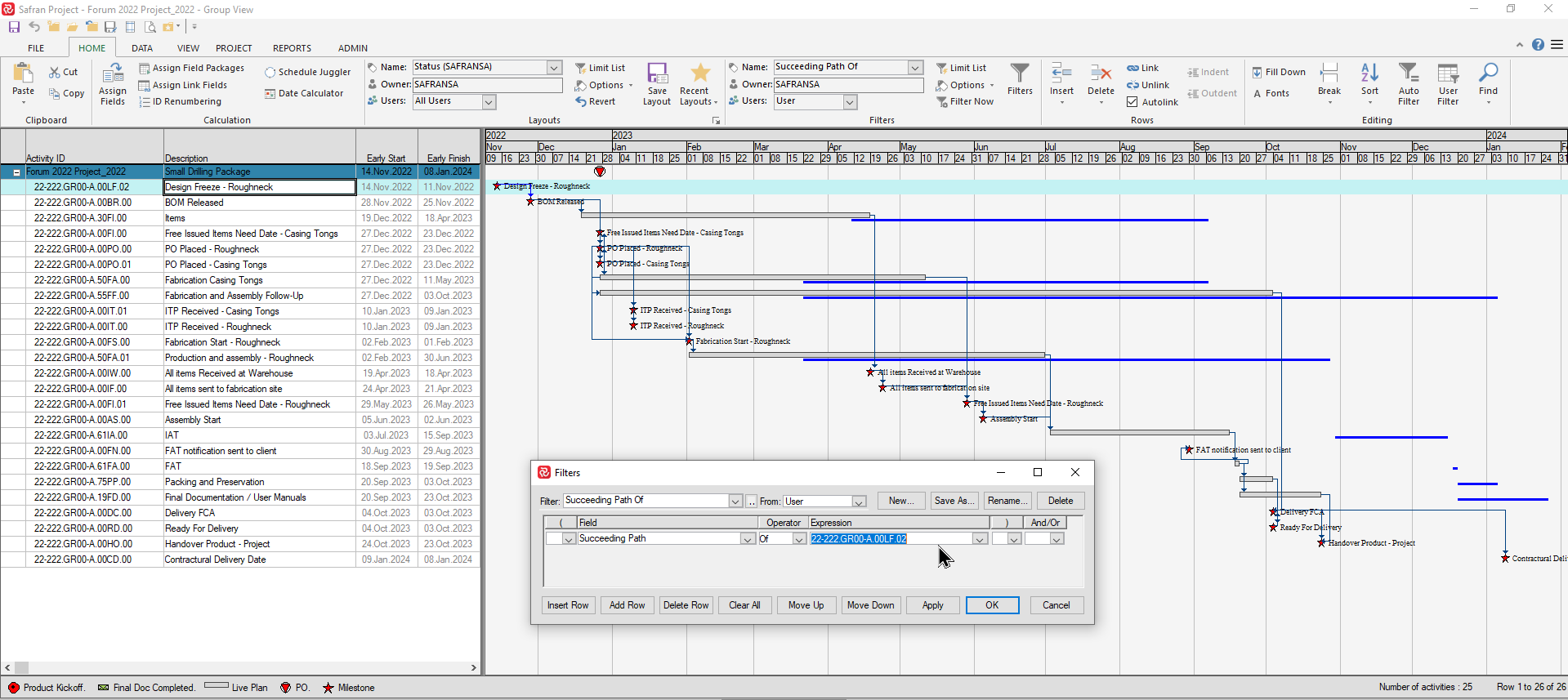
By combining the two in a filter you can focus on all activities logically related to two or more activities as shown in the picture below:

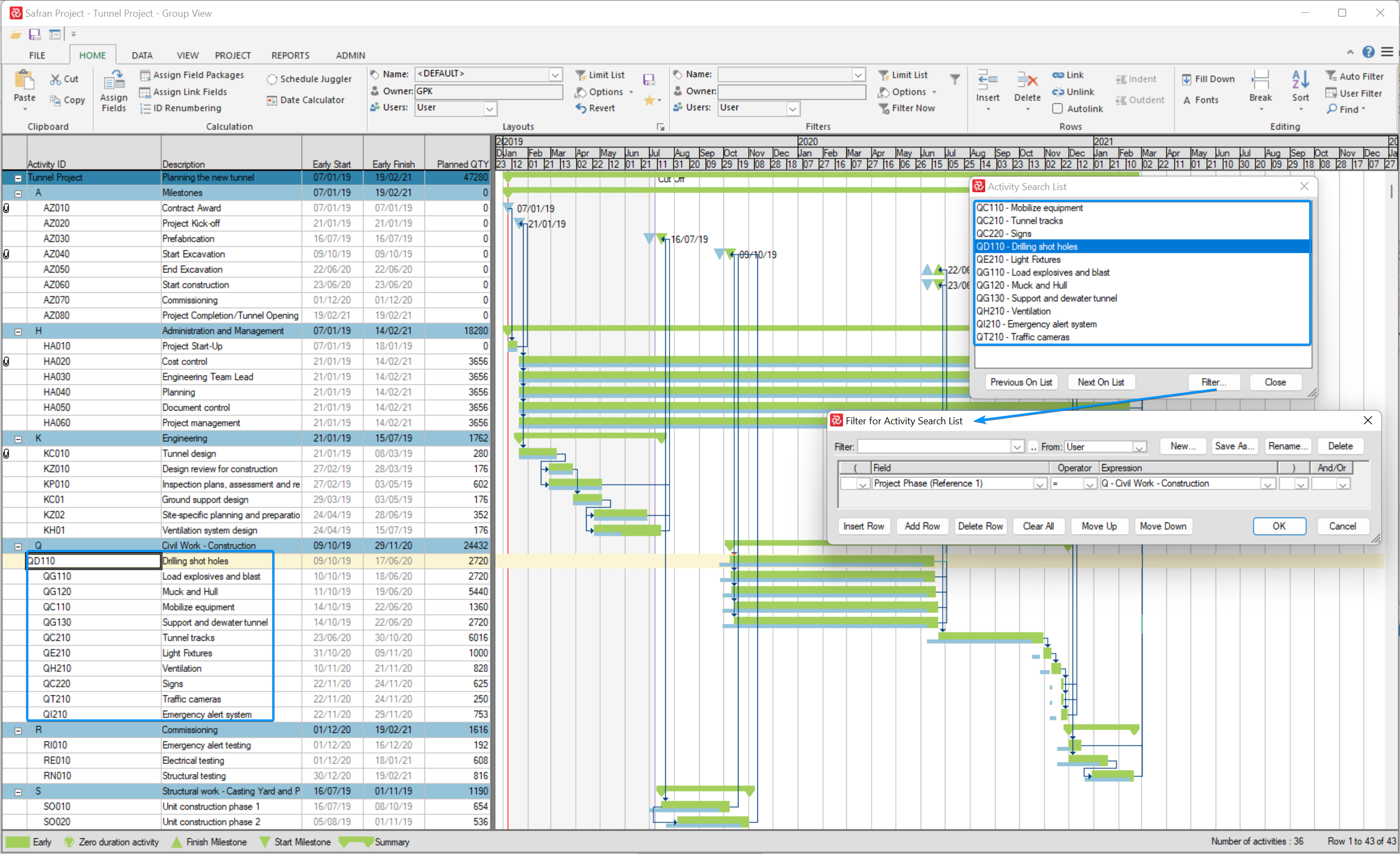
Activity Search List
The activity search list allows you to create a subset of activities to browse or investigate and still have all activities selected in the Barchart Editor. This will enable you to browse predecessors or successors, follow the logic outside the activities in the search list, and then revert to the search list and use this as your criteria for investigating the schedule.
Applying the selection criteria as a Filter to the Barchart Editor would allow you to see and investigate the activities that match the requirements.
Opening the Search List.
The Activity Search List option is available from the Filter section on the Home tab. Select 'Options' and then 'Activity Search List.'
The activity Search list window opens with all activities in the project as default. The Activity Search List displays 'Activity ID' and 'Description'. Activities are sorted by Activity ID. The window is resizable and stays on top of the Barchart Editor until closed.
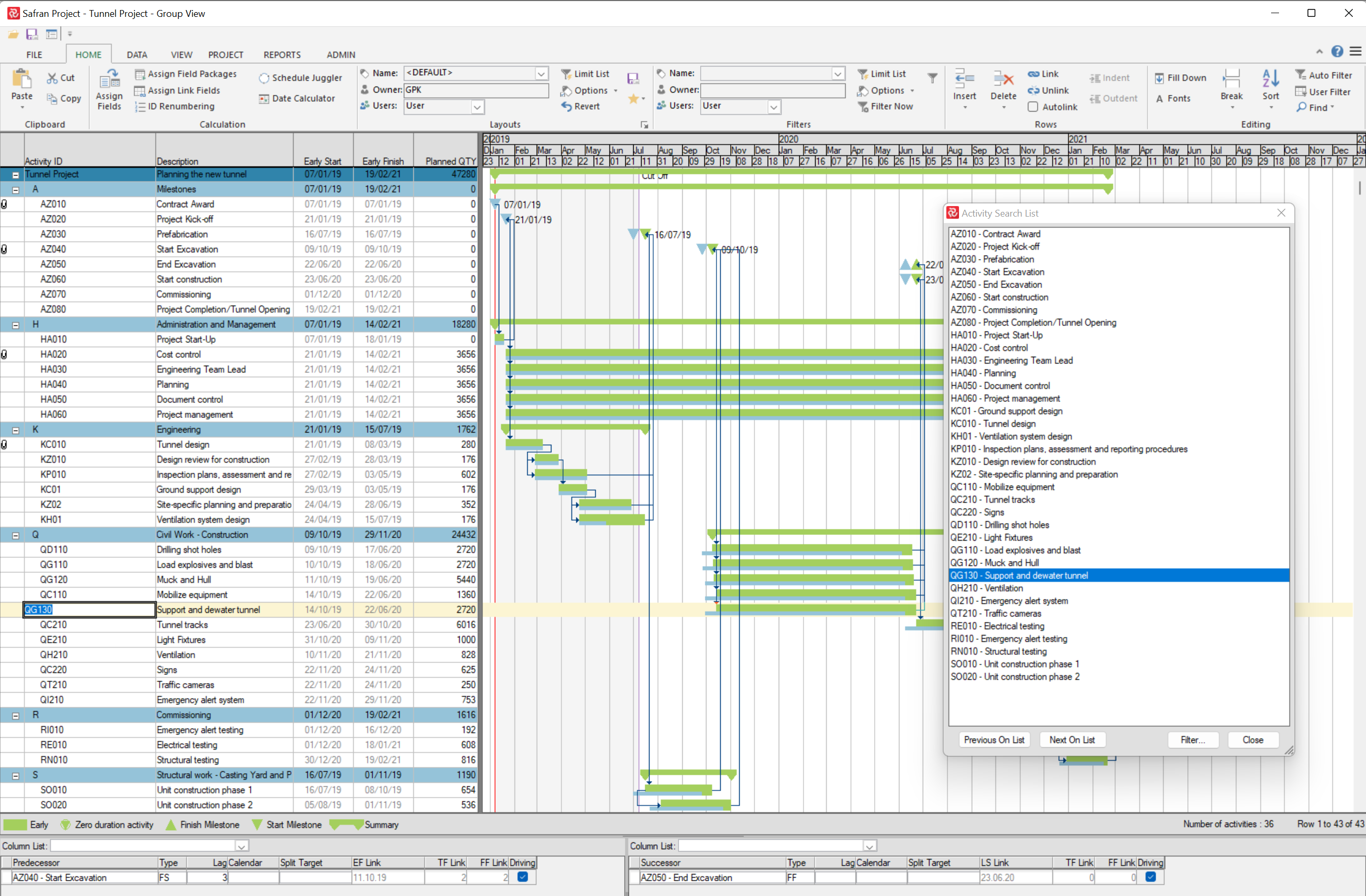
Navigating
The Activity Search List window is synchronized with the Barchart Editor in such a way that if you select an activity in the Search list, it will be highlighted in the Barchart Editor, or if you choose an activity from the Editor, it will be highlighted in the Search list if it is a part of the activities listed in the search list.
- You can click on any activity in the search List window, and it will highlight the activity in the Barchart Editor.
- You can use 'Previous On List' to navigate the activity above the selected activity.
- You can use 'Next On List' to navigate to the activity below the currently selected activity.
Creating Your List - Filtering
You usually will not navigate the Activity Search List with all activities selected for focus. To create a selection of activities, press the Filter button to select previously stored filter expressions that fit your task. Use the filter window to generate an ad-hock filter or create a new filter to be stored.
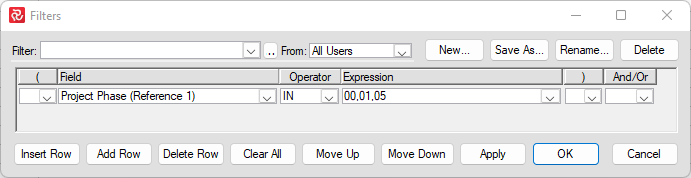
Example of filter applied to create a list of activities for Phase= Q - Civil Work - Construction.